Facial recognition technology is rapidly gaining traction as a reliable and secure method of authentication. With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, the ability to identify individuals through their unique facial features has become more accurate and efficient. This biometric solution not only simplifies the authentication process but also enhances security measures across various sectors, from financial services to personal devices. As concerns around privacy and data protection rise, understanding how facial recognition works and its applications is essential for embracing this innovative technology.
Understanding Facial Recognition Technology
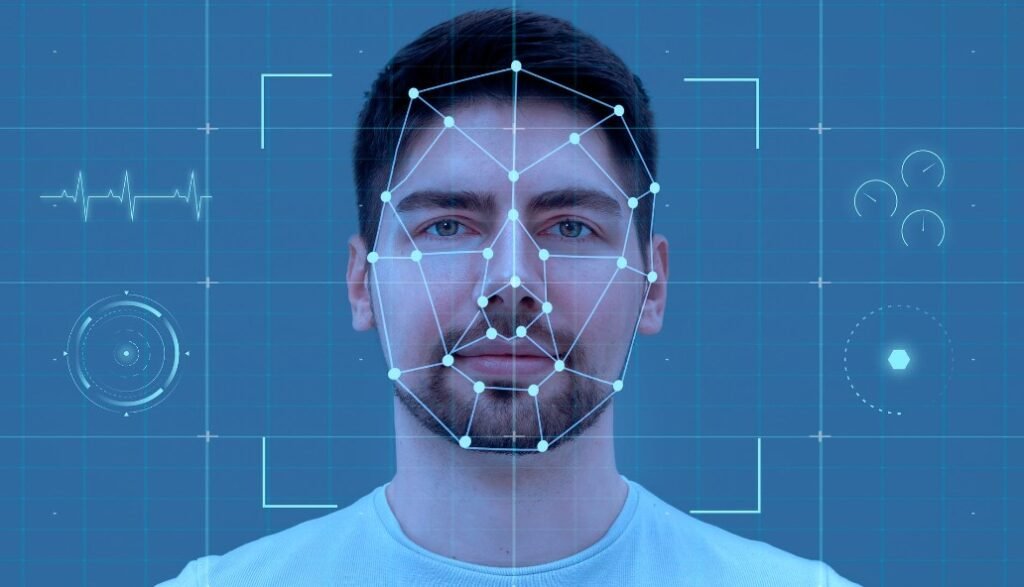
Facial recognition is a biometric technology that uses algorithms to identify a person by analyzing their facial features. The process begins with the capture of an image, commonly through a camera. The system then detects and isolates the face from the background, followed by feature extraction, where key facial landmarks—such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the jaw, and the contour of the cheeks—are measured. These measurements create a unique facial signature, which is compared against a database of stored images to verify the individual’s identity.
Advantages of Facial Recognition in Authentication
Increased Security
One of the primary benefits of using facial recognition for authentication is the enhanced security it provides. Unlike traditional methods such as passwords or PINs, which can be forgotten or stolen, facial recognition relies on unique biological traits. This drastically reduces the risk of unauthorized access, as replicating someone’s facial features is far more challenging than acquiring codes or passwords.
Convenience and Speed
Facial recognition technology offers unparalleled convenience. Users can authenticate their identity within seconds simply by looking at a camera, eliminating the need to remember complex passwords or carry physical tokens. This speed not only improves user satisfaction but also streamlines processes across various applications, such as airport security, mobile devices, and access control systems.
Applications of Facial Recognition
Banking and Financial Services
The banking sector is increasingly adopting facial recognition technology to secure transactions and customer interactions. By enabling biometric authentication, financial institutions can reduce fraud and identity theft while enhancing the customer experience. For example, customers can authorize payments or access their accounts through facial recognition, offering a seamless and secure banking experience.
Mobile Devices
Mobile phones equipped with facial recognition technology have become commonplace, allowing users to unlock their devices with ease. This feature not only enhances user experience but also adds a layer of security, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information stored on their devices.
Law Enforcement
Facial recognition is also employed by law enforcement agencies to identify suspects and enhance public safety. By comparing real-time footage from surveillance cameras with existing databases, authorities can quickly locate individuals of interest, thus enabling faster responses to potential threats.
Addressing Privacy Concerns
Despite the numerous benefits of facial recognition technology, it is crucial to acknowledge the privacy concerns it raises. Unauthorized surveillance and data misuse are potential risks that must be addressed through robust regulations and ethical guidelines. Organizations implementing facial recognition should prioritize transparency and ensure that sensitive data is stored securely and used solely for intended purposes.
The Future of Facial Recognition
As facial recognition technology continues to evolve, its potential applications are vast. With growing integration into smart cities, social media platforms, and personalized marketing, it is essential for stakeholders to develop responsible practices that protect individuals’ privacy and civil liberties. The focus must remain on creating a balance between leveraging innovative technology and safeguarding human rights.
Conclusion
Facial recognition technology stands poised to revolutionize the way we authenticate our identities in an increasingly digital world. With its remarkable precision, convenience, and security advantages, it is an appealing alternative to traditional methods of authentication. However, as this technology proliferates, it is imperative to address the associated privacy concerns proactively to ensure it is deployed ethically and responsibly. Embracing facial recognition can unlock new horizons for security and user experience, but only if it is implemented with care and consideration for the rights of individuals. So, be prepared to see more of this