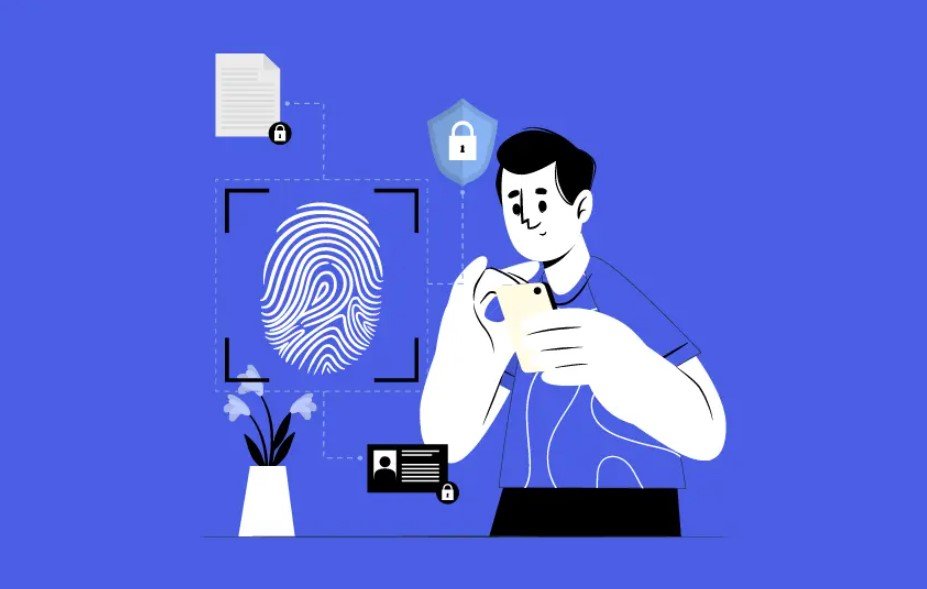
The quest for enhanced security is ever-present in today’s technology-driven world. With a surge in data breaches and identity theft, organizations and individuals alike are turning to innovative solutions that traditional methods fail to provide. Biometrics, which involves the identification of individuals based on their unique physical or behavioral characteristics, is emerging as a cornerstone of modern security measures. This technology leverages attributes such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice patterns to create a robust mechanism for authentication, thereby fortifying safety across various sectors.
Understanding Biometrics
Biometrics operates on the premise that each person possesses distinct features, making them ideal for identification and verification purposes. There are two main categories of biometrics: physiological and behavioral. Physiological traits include fingerprints, facial structure, iris patterns, and even DNA, while behavioral traits encompass characteristics like voice recognition, keystroke dynamics, and gait analysis. By implementing biometric systems, organizations can deliver a layer of security that password-based systems simply cannot match.
Advantages of Biometrics
Enhanced Security
One of the primary benefits of biometrics is its potential for enhanced security. Unlike passwords or PINs, which can be forgotten, stolen, or hacked, biometric identifiers are unique to each individual. This uniqueness provides a much higher assurance of identity verification, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Convenience and Speed
Another compelling advantage is the convenience and speed of biometric authentication. Users can gain instant access to secured systems without the need to remember complex passwords or carry additional authentication devices. This streamlined process not only saves time but also enhances user satisfaction.
Cost-Effectiveness
While there may be upfront costs associated with implementing biometric technology, these systems can lead to long-term savings. By reducing the incidence of security breaches and the associated costs of recovery, organizations may find that the return on investment from adopting biometric solutions is significant.
Applications of Biometrics
Workplace Security
Biometric systems are increasingly being integrated into workplace security measures. Companies are deploying fingerprint scanners and facial recognition technology at entry points to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive areas. This level of scrutiny creates a safer work environment and protects valuable data and assets.
Financial Transactions
In the financial sector, biometric authentication is transforming the way transactions are conducted. Banks are employing fingerprint and facial recognition technologies for everything from account access to in-person transactions. This shift not only proves beneficial for security but also adds convenience for customers, allowing them to engage with their finances seamlessly.
Mobile Device Security
As mobile devices continue to proliferate, so does the need for robust security mechanisms. Most modern smartphones come equipped with biometric authentication technologies, such as fingerprint scanners and facial recognition capabilities. These features provide users with an extra layer of protection for personal and sensitive information, helping to safeguard against unauthorized access.
Healthcare Confidentiality
In the healthcare sector, patient confidentiality is paramount. Biometric identification systems can help ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive patient information. Implementing such systems helps healthcare facilities comply with regulations while safeguarding patient privacy and improving overall trust in the healthcare system.
Challenges and Considerations
Privacy Concerns
Despite the numerous benefits, biometric technology also raises concerns related to privacy. The storage and management of biometric data must be handled with extreme care to prevent unauthorized use. Organizations must establish robust policies and practices to safeguard this sensitive information.
Cost of Implementation
While the long-term benefits may outweigh the initial costs, the implementation of biometric systems can present a financial burden for smaller organizations. Weighing the costs against the intended security outcome is crucial for decision-makers looking to adopt this technology.
Potential for Errors
Like any other technology, biometric systems are not infallible. Factors such as environmental conditions, user behavior, or technology malfunctions can lead to false rejections or acceptances. Organizations must be prepared to address these potential errors to maintain trust in the biometric systems.
Future Trends in Biometrics
Continuous Authentication
The future of biometric technology is leaning toward continuous authentication, where systems will constantly verify a user’s identity through various means while they interact with the device or service. This approach could further strengthen security by minimizing the risk of unauthorized access after initial login.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning can enhance biometric systems by improving their accuracy and efficiency. AI can adapt biometric algorithms based on user behavior patterns, making them smarter at recognizing identities while reducing the chances of fraud.
Multi-Factor Biometrics
As security concerns grow, the trend towards multi-factor biometrics is becoming more prevalent. Combining various biometric indicators, such as facial recognition and voice analysis, can offer layered security that is significantly more difficult to breach. This trend will likely see widespread adoption across various sectors.
Conclusion
Biometric technology offers a revolutionary approach to enhancing safety and security in our increasingly digital world. By harnessing unique human attributes for identification and authentication, organizations can set up robust defenses against unauthorized access and identity theft. While there are challenges to consider, the benefits of biometric safety measures are undeniable, urging industries to adapt and innovate continuously. As biometric technology evolves, staying informed about its capabilities and advancements will be essential for any entity invested in securing their critical assets and information.